BEIJING, Nov. 19, 2024 /PRNewswire/ -- With the support of the RiDYMO® platform, we are able to comprehensively explore various potential targets in drug development, including protein-protein interactions, kinases, GPCRs, ion channels, and transcription factors.
Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) is a highly conserved serine/threonine protein kinase that plays a crucial role during cellular mitosis[1]. It is overexpressed in various malignancies, including colorectal cancer[2], pancreatic cancer[3], and breast cancer, and its high expression is associated with poor prognosis. Consequently, PLK1 has emerged as a promising target in cancer drug development, with numerous candidates currently in the pipeline worldwide. Among these, Cardiff Oncology's onvansertib (PCM-075) has shown the most significant progress, displaying encouraging efficacy results in clinical treatment for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC).
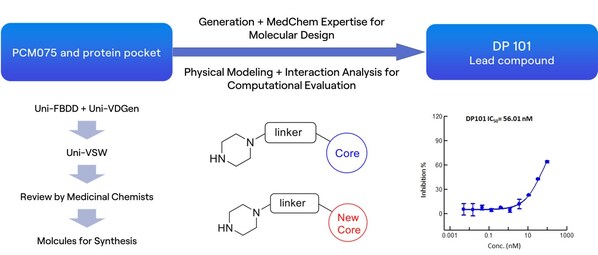
The RiDYMO® platform, a next-generation computational drug design platform developed by DP Technology, based on AI for Science, provides robust end-to-end support for hit discovery and optimization by integrating multiple artificial intelligence techniques, physical algorithms, and experimental validation. In this study, we referred to the co-crystal complex of PLK1 and PCM075 (2YAC) and utilized the RiDYMO platform's comprehensive capabilities to synthesize and test under 100 compounds, leading to the identification of preclinical candidate compounds with potential clinical value and significantly accelerating the drug development process.
We first conducted an in-depth analysis of the interactions between PCM-075 and the PLK1 protein. Preserving key interactions, we applied molecular generation, evaluation, and screening techniques to obtain a novel scaffold, the lead compound DP101, which exhibited an activity of 56 nM.
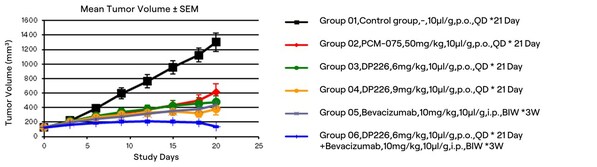
Next, during the optimization process based on the structure of DP101, we modified several sites on the scaffold, including hydrogen bonding networks (R3) and hydrophobic group encapsulation zones (R1 & R2). Experimental data showed a high consistency between computational predictions and experimental results, demonstrating the platform's practicality in optimizing kinase inhibitors.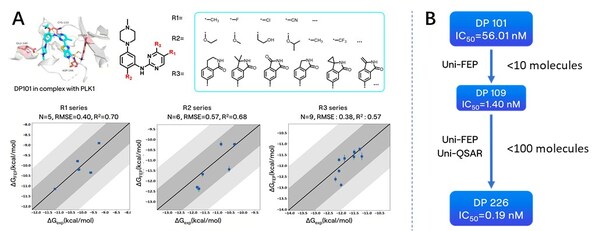
Figure A: Optimization and FEP prediction for R1, R2, and R3, with dark gray areas indicating a 1 kcal error range and light gray areas representing a 2 kcal error range; B: Overall molecular optimization process based on the DP101 scaffold
About the RiDYMO® Hit Discovery and Optimization Platform
RiDYMO® is a state-of-the-art hit discovery and optimization platform developed by DP Technology, leveraging the principles of AI for Science. It employs the proprietary Hermite® computational drug design software to elucidate the dynamics of "undruggable" targets and explores a broader chemical space encompassing small molecules, macrocycles, and cyclic peptides. By integrating advanced artificial intelligence, physical algorithms, and high-throughput experimentation, the platform excels in designing oral macrocyclic compounds and rapidly delivers innovative drug candidates.
As one of its core algorithms, Reinforced Dynamics (RiD)[4] has a significant advantage in the sampling efficiency of molecular dynamics simulation. By fully leveraging the high-dimensional representation capabilities of neural networks, RiD can efficiently capture dynamic conformational changes in complicated biomolecular systems. Previously, the core RiD algorithm of the platform was published in Nature Computational Science. The study demonstrated that RiD could achieve a more comprehensive free energy surface within 1.86 μs, compared to 100 μs required by traditional MD methods, representing nearly a hundredfold increase in efficiency.
RiDYMO® has been successfully employed in various projects, including the development of c-Myc small molecules, GPX4 small molecules, and β-catenin cyclic peptides, demonstrating its strong potential in innovative drug discovery.
For more information, please visit our website.
(https://www.dp.tech/en/services/medicine).
About Hermite
Hermite® is a next-generation computational drug design platform developed by DP Technology, powered by AI for Science, to provide a comprehensive solution for drug design. Hermite® integrates industry-leading tools such as the Free Energy Perturbation module, Uni-FEP, and the ultra-high-throughput virtual screening tool, Uni-VSW, supporting key stages of drug discovery, from protein structure prediction and target validation, to hit discovery and lead optimization.
The platform offers an interactive, web-based molecular visualization experience, with detailed management of projects, teams, and data. It features full compliance certification, multi-tier security measures, and supports both cloud-based and private deployment options.
Hermite® is trusted by over 60% of leading pharmaceutical companies in China, applied across more than 50 drug pipelines. To date, industry users have performed over 200,000 Uni-FEP calculations on the Hermite® platform.
For more information, please visit: https://www.dp.tech/en/product/hermite
About DP Technology
At DP Technology, we're at the forefront of integrating artificial intelligence into scientific research and industrial R&D. Our "AI for Science" initiative is redefining how we tackle complex scientific challenges, making groundbreaking discoveries more accessible and actionable.
We've developed the "DP Particle Universe," a suite of advanced pre-trained models that seamlessly connect cutting-edge research with real-world industrial applications. Our software suite includes: Bohrium® Scientific Computing Space Station, Hermite® Computational Drug Design Platform, RiDYMO® Hit Discovery Platform, and Piloteye® Battery Design Automation Platform. Together, these platforms form a robust foundation for industrial innovation and an open ecosystem for AI in science, fostering advancements in key areas such as drug discovery, energy, materials science and information technology.
| References: |
| 1. Polo on the Rise-from Mitotic Entry to Cytokinesis with Plk1. Dev Cell. 2008 May;14(5):646-59. |
| 2. Polo-like kinase 1 expression is a prognostic factor in human colon cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2005 Sep 28;11(36):5644-50. |
| 3. Identification of human polo-like kinase 1 as a potential therapeutic target in pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2004 May;3(5):641-6. |
| 4. Efficient sampling of high-dimensional free energy landscapes using adaptive reinforced dynamics. Nat Comput Sci. 2022 Jan;2(1):20-29. |